orbitals s p d f|Iba pa : Baguio The simplest atomic orbitals are those that are calculated for systems with a single electron, such as the hydrogen atom. An atom of any other element ionized down to a single . Tingnan ang higit pa 1 talking about this. nosTEAM PC Games Forum Ask for game support on https://twitter.com/nosteamgames.
PH0 · shape of p orbital
PH1 · s p d f quimica
PH2 · orbitals chemistry
PH3 · o que são orbitais
PH4 · numero de orbitais
PH5 · niveles s p d f
PH6 · geometria dos orbitais
PH7 · atomic orbital diagram
PH8 · Iba pa
Information about Dota 2 team TSM. TSM statistics, roster, and history.
orbitals s p d f*******The simple names s orbital, p orbital, d orbital, and f orbital refer to orbitals with angular momentum quantum number ℓ = 0, 1, 2, and 3 respectively. These names, together with the value of n, are used to describe the electron configurations of atoms. Tingnan ang higit paIn quantum mechanics, an atomic orbital is a function describing the location and wave-like behavior of an electron in an atom. This function describes the electron's charge distribution around the atom's nucleus, and can be . Tingnan ang higit paThe term "orbital" was coined by Robert S. Mulliken in 1932 as short for one-electron orbital wave function. Niels Bohr explained around . Tingnan ang higit paThe simplest atomic orbitals are those that are calculated for systems with a single electron, such as the hydrogen atom. An atom of any other element ionized down to a single . Tingnan ang higit paSimple pictures showing orbital shapes are intended to describe the angular forms of regions in space where the electrons occupying . Tingnan ang higit pa
With the development of quantum mechanics and experimental findings (such as the two slit diffraction of electrons), it was . Tingnan ang higit paOrbital notation and subshellsOrbitals have been given names, which are usually given in the form:$${\displaystyle X\,\mathrm {type} \ }$$where X . Tingnan ang higit pa
Because of the quantum mechanical nature of the electrons around a nucleus, atomic orbitals can be uniquely defined by a set of . Tingnan ang higit pa
Learn about the types, shapes, and energy levels of atomic orbitals, and how to determine their quantum numbers. Find out how to place electrons in orbitals according to Hund's . p orbitals. Not all electrons inhabit s orbitals (in fact, very few electrons live occupy s orbitals). At the first energy level, the only orbital available to electrons is the .
Every subshell has a # of orbits s/p/d/f that can each hold 2 electrons each (one has the opposite spin of the other). The first shell (of all atoms) has 1 subshell of s-orbitals .orbitals s p d fLearn about the different shapes and properties of atomic orbitals, the mathematical functions that describe the wave nature of electrons in an atom. See boundary surface .
orbitals s p d f Iba paThe s subshell has 1 orbital that can hold up to 2 electrons, the p subshell has 3 orbitals that can hold up to 6 electrons, the d subshell has 5 orbitals that hold up to 10 electrons, and the f subshell has 7 orbitals with 14 .The principal quantum number is named first, followed by the letter s, p, d, or f as appropriate. These orbital designations are derived from corresponding spectroscopic .
An orbital is a space where a specific pair of electrons can be found. We classified the different Orbital into shells and sub shells to distinguish them more easily. This is also due to . About. Transcript. Electron configurations describe where electrons are located around the nucleus of an atom. For example, the electron configuration of lithium, 1s²2s¹, tells us that lithium has two electrons in the 1s subshell and one electron in the .Learn about the shapes, sizes and energies of s,p,d,f orbitals, the regions of space where electrons are most likely to be found. See examples, diagrams and explanations of how to arrange electrons in different subshells and .The four different orbital forms (s, p, d, and f) have different sizes and one orbital will accommodate up to two electrons at most. The orbitals p, d, and f have separate sub-levels and will thus accommodate more .Iba pa2) Orbitals are combined when bonds form between atoms in a molecule. There are four types of orbitals that you should be familiar with s, p, d and f (sharp, principle, diffuse and fundamental). Within each shell of an .
If there are more electrons after the 1s, and 2s orbitals have been filled, each p orbital will be filled with one electron first before two electrons try to reside in the same p orbital. This is known as Hund's rule. Figure 12.9.3 .
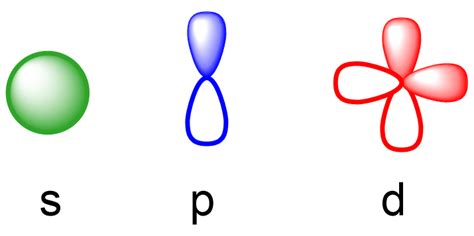
The four chemically important types of atomic orbital correspond to values of l = 0, 1, 2, and 3. Orbitals with l = 0 are s orbitals and are spherically symmetrical, with the greatest probability of finding the electron occurring at the nucleus. All orbitals with values of n > 1 and l = 0 contain one or more nodes. Like the s and p orbitals, as n increases, the size of the d orbitals increases, but the overall shapes remain similar to those depicted in Figure \(\PageIndex{5}\). f Orbitals (l=3) Principal shells with n = 4 can have subshells with l = 3 and m l values of −3, −2, −1, 0, +1, +2, and +3.
Orbital Energies and Atomic Structure. The energy of atomic orbitals increases as the principal quantum number, \(n\), increases. In any atom with two or more electrons, the repulsion between the electrons makes energies of subshells with different values of \(l\) differ so that the energy of the orbitals increases within a shell in the order . Algunos ejemplos de orbitales s, p, d y f, con orientaciones diferentes. Cada tipo de orbital puede albergar un número de electrones específico. Por ejemplo, el orbital s puede contener hasta 2 electrones por cada nivel de energía, mientras que el orbital p alberga hasta 6 electrones. Si tomamos el oxígeno como referencia, .Vacant s, d, and f orbitals have been shown explicitly, as is occasionally done, to emphasise the filling order and to clarify that even orbitals unoccupied in the ground state (e.g. lanthanum 4f or palladium 5s) may be occupied and bonding in chemical compounds. (The same is also true for the p-orbitals, which are not explicitly shown because .
Formas de orbitais e padrões de densidade de elétrons. Os orbitais s são esféricos, enquanto os orbitais p são polares e orientados em direções particulares (x, y e z).Pode ser mais simples pensar nessas duas letras em termos de formas orbitais ( d e f não são descritos tão prontamente).No entanto, se você olhar para uma seção . El número cuántico azimutal l, asociado al momento angular del electrón (cantidad de movimiento angular: el producto de su masa por su velocidad de rotación) que se expresa en letras; s para l =0; p para l =1, d para l =2, f para l =3. La nomenclatura del número l con letras tiene su origen en el estudio de los espectros de los metales .

The letter tells you which orbital it is, eg s, p, d or f The superscript number tells you how many electrons are in that orbital 1s^2 means 2 electrons are in the 1s orbital 1s^2 2s^2 .d and f orbitals. In addition to s and p orbitals, there are two other sets of orbitals which become available for electrons to inhabit at higher energy levels. At the third level, there is a set of five d orbitals (with . Explicação: Cada orbital é indicado por um número e uma letra. O número indica o nível de energia do elétron no orbital. Assim, 1 refere-se ao nível de energia mais próximo do núcleo; 2 refere-se ao .Jumlah dan bentuk orbital pada setiap sub kulit s, p, d, dan f berbeda-beda. Jumlah orbital pada sub kulit s, p, d, dan f berturut-turut adalah 1, 3, 5, dan 7. Setiap satu orbital dapat memuat paling banyak dua leketron. Sehingga, banyak elektron maksimal yang menempati sub kulit s, p, d, dan f berturut-turut adalah 2, 6, 10, dan 14 elektron.Les orbitales s, p, d, f. La physique montre que dans la structure de l’atome , les couches électroniques sont réparties en niveaux d’énergie : les orbitales, telles que : Sur l’orbitale s = 2 électrons. p =6 électrons. d= 10 électrons. f = 14 électrons. les électrons sont liés, par leur spin, en paires. La forma de un orbital es denotada por las letras s, p, d, y f. En la química orgánica, tratamos principalmente con elementos en la segunda fila de la tabla períodica más el hidrógeno. . Por ejemplo, un átomo del elemento borón, con 5 electrones, tiene la configuración electrónica 1s 2 2s 2 2p x 1: el orbital 1s contiene dos . The first two are familiar, the s orbital and p orbitals. The third, the d orbital, is discussed later. Below are representations of the 3s orbital, and the 3p orbitals. As the 2s orbital was slightly different in shape from the 1s orbital due to the introduction of a node, so the 3s and 3p orbitals differ slightly in shape from the 2s and 2p .
Çekirdek etrafında elektronlar belirli enerji seviyelerinde bulunur. Elektronların çekirdek etrafında bulunma olasılığının en yüksek olduğu bölgeye orbital denir. Açısal momentum kuantum sayısına(l) bağlı olarak s, p, d ve f orbitalleri olmak üzere dört grupta incelenir. s orbitali Küreseldir. En fazla iki elektron alır. Baş kuantum sayısı büyüdükçe s .
Fast Track Saver Account . This does not include cheques written or deposited, branch cash withdrawals, transfers or payments to any BOQ account or to a non-BOQ account via Internet Banking, in branch or at ATMs, transfer of funds to accounts held at an overseas bank, pending Visa Debit Card transactions and BOQ Credit Card transactions. .
orbitals s p d f|Iba pa